Denmark loan interest rate: Drawing from authoritative data provided by Danmarks Nationalbank, Denmark’s central banking institution, this article explores the nation’s loan interest rate journey over the years.
Renowned for its vibrant economy and high standard of living, Denmark has experienced an intriguing ebb and flow in its lending rates. This data from the Nationalbank gives us an unparalleled insight into the nation’s monetary strategies, challenges, and triumphs.
Related: Loans in Denmark
Let’s delve into these rates’ fluctuating patterns, peaks, and troughs over time.
From Peaks to Valleys
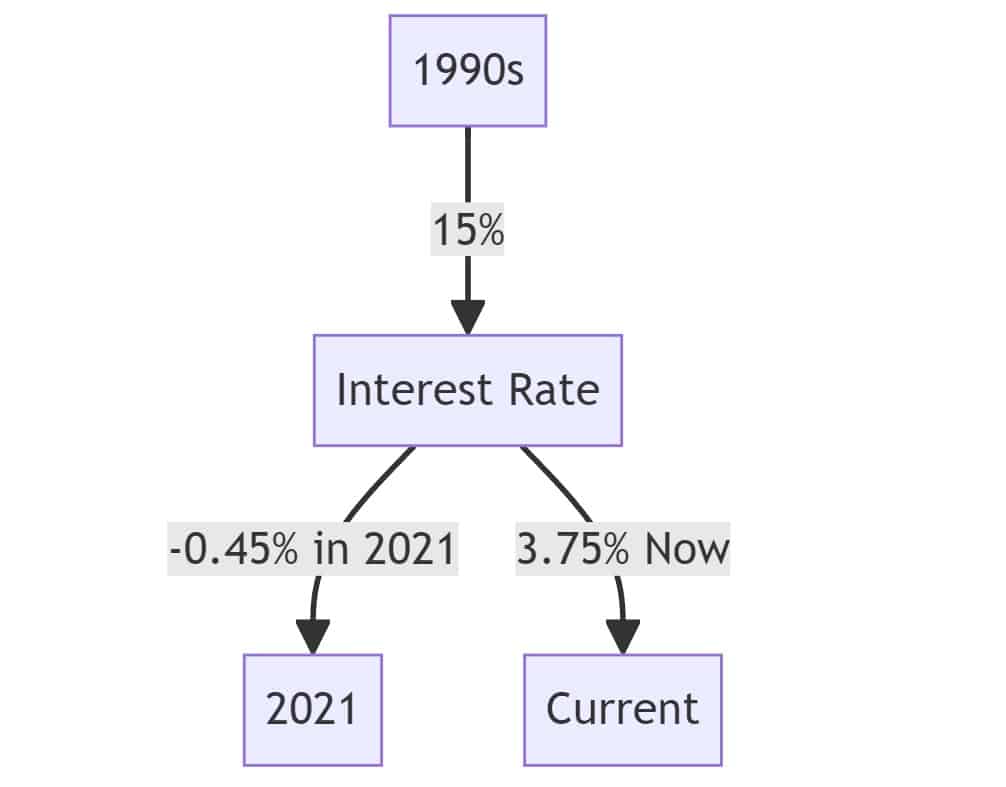
The data reveals that the highest interest rate recorded was a staggering 15% in November 1992, signaling a tight monetary stance, possibly aimed at curbing inflation or stabilizing the currency. Contrastingly, the most recent years have seen rates dive into the negatives, hitting a low of -0.45% in October 2021. This negative rate suggests a strategy to stimulate borrowing and combat deflationary pressures.
The 1990s: A Decade of Highs
The early 1990s showcased some of the highest interest rates, with 1992 alone seeing rates fluctuating between 9.85% to 15%. The sharp drop from 15% in November to 9.90% in December 1992 indicates a rapid policy shift, possibly due to external economic pressures or domestic concerns.
The 2000s: Stabilization and Steady Decrease
The early 2000s started with rates hovering around the 5% mark. However, as the decade progressed, Denmark’s interest rates began a steady descent, with the occasional spike, settling around the 1% range by 2009.
2010s to Present: Into the Negative Territory
The 2010s introduced a new phenomenon: negative interest rates. With rates like -0.45% in 2021, the Nationalbank showcased its aggressive stance to encourage spending and investments. These rates slowly crept up, and by September 2023, they stabilized at 3.75%.
Concluding Thoughts
Denmark’s historical loan interest rates reveal a tale of a nation’s evolving economic strategies, challenges, and triumphs. From the soaring highs of the early ’90s to the negative lows of the 2010s, Denmark’s adaptive monetary policies highlight its commitment to maintaining economic stability and growth.